Have you ever wondered what really goes on in your body and how it relates to your sexual health? Vaginal fluid is often shrouded in mystery, leading many to question its composition and function. One common query that surfaces is: Does vaginal fluid contain protein? The answer might surprise you and could have implications for your overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind vaginal fluid, exploring its components, benefits, and the role it plays in female health. From understanding the protein content to uncovering dietary tips that enhance lubrication, we’ll cover everything you need to know. Whether you’re curious about vaginal health or seeking ways to improve your intimate life, this guide is tailored to provide clear, informative answers that resonate with your interests. So, let’s unlock the secrets of vaginal fluid and discover the fascinating truths behind this essential aspect of female biology.
What You Will Learn
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover:
- The composition of vaginal fluids and whether they contain protein.
- The benefits of vaginal fluid.
- Comparison of vaginal fluid and male discharge.
- Nutritional aspects of vaginal and seminal fluids.
- Practical advice for maintaining vaginal health and wellness.
- Common myths and misconceptions surrounding vaginal fluid.
- Tips for enhancing vaginal health through diet and lifestyle.
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of vaginal health!
Does Vaginal Fluid Have Protein?
Vaginal fluid, often dismissed in discussions about women’s health, plays an essential role in sexual function and reproductive health. But what about its protein content?
Understanding Vaginal Fluid Composition
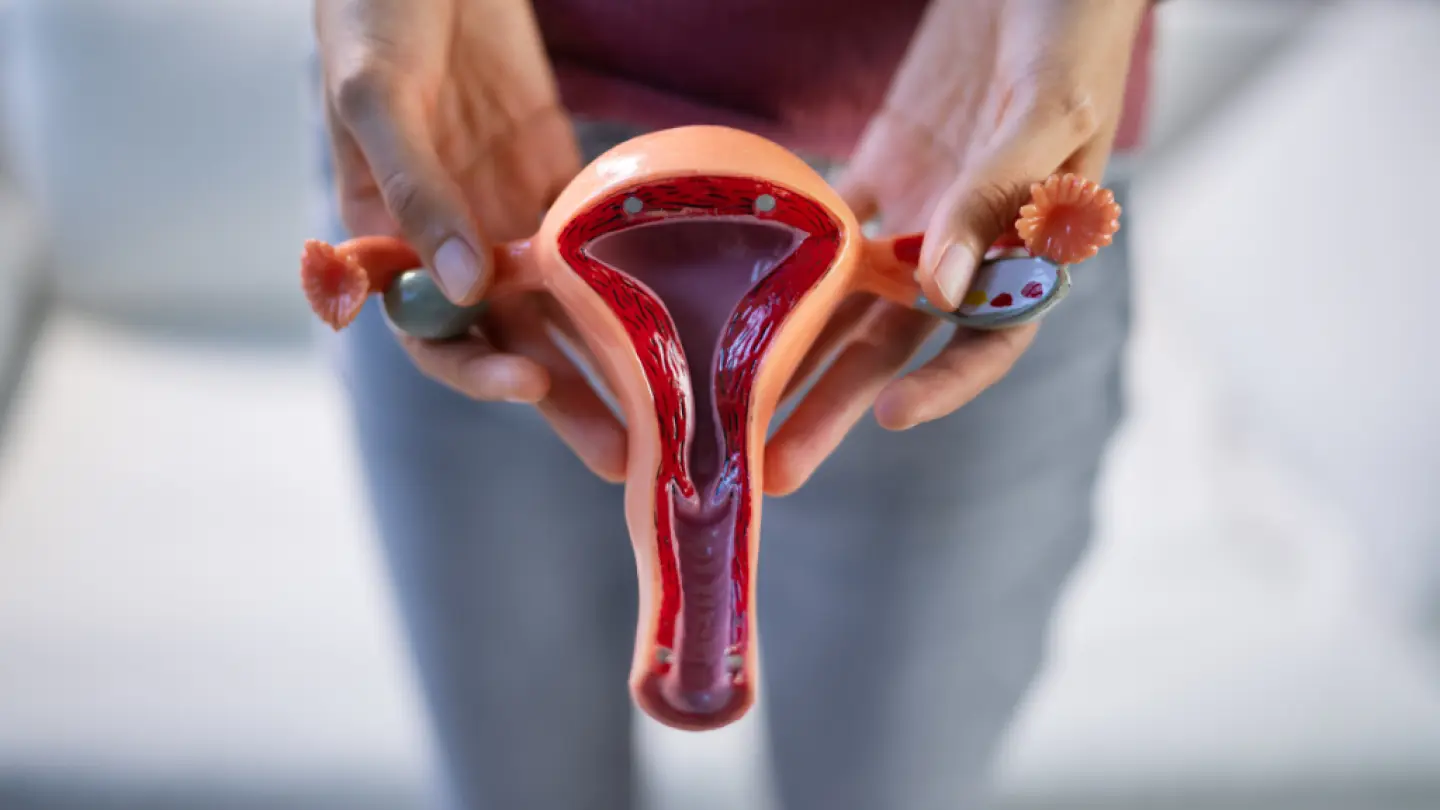
Vaginal fluid is made up of a complex mix of water, cells, bacteria, and various substances, including proteins. The primary proteins found in vaginal fluid are secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA) and lactoferrin. These proteins serve vital functions in protecting against infections and maintaining a healthy vaginal environment.
The Role of Proteins in Vaginal Health
Proteins are crucial for various bodily functions, including immune response and tissue repair. In the context of vaginal fluid, proteins like IgA play a role in mucosal immunity, helping to defend against pathogens that could cause infections. Lactoferrin, another important protein found in vaginal fluid, has antimicrobial properties that contribute to maintaining a healthy balance of bacteria in the vagina.
How Much Protein Is in Vaginal Fluid?
While the exact protein content can vary from person to person, studies have shown that vaginal fluid contains approximately 1-2 grams of protein per liter. This relatively low concentration highlights that while vaginal fluid does have protein, it is not a primary source of dietary protein.
Factors Influencing Protein Content
The protein content in vaginal fluid can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones play a significant role in vaginal health. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels throughout the menstrual cycle can affect the composition of vaginal fluid, including its protein content. For instance, during ovulation, estrogen levels peak, which can lead to increased secretion of vaginal fluid that is rich in proteins.
- Age: As women age, especially during and after menopause, the body produces less estrogen, which can lead to changes in the vaginal environment. This may result in reduced production of vaginal fluid and a change in its protein content.
- Diet and Hydration: A woman’s diet and overall hydration status can also impact the composition of vaginal fluid. Consuming a balanced diet with adequate hydration supports the body’s functions, including the production of vaginal secretions.
What Is Vaginal Fluid Made Of?
To fully appreciate the role of vaginal fluid, it’s crucial to understand its components. Vaginal fluid consists of:
- Water: The primary component, making up about 90% of the fluid.
- Mucins: These are glycoproteins that contribute to the viscosity of the fluid, providing lubrication during sexual activity.
- Electrolytes: Sodium, potassium, and calcium are essential for maintaining the right pH balance.
- Bacteria: The vaginal microbiome plays a crucial role in preventing infections and maintaining a healthy environment.
- Proteins: As mentioned earlier, proteins like IgA and lactoferrin are present.
This combination ensures that the vaginal environment remains healthy and balanced, facilitating reproductive processes.
The Importance of the Vaginal Microbiome
The vaginal microbiome consists of various microorganisms, predominantly lactobacilli, which help maintain an acidic environment. This is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevention of Infections: The presence of beneficial bacteria helps to outcompete harmful pathogens, reducing the risk of infections.
- Balancing pH Levels: The healthy vaginal microbiome keeps the pH in the appropriate range (typically between 3.8 and 4.5), which is essential for overall vaginal health.
- Aiding Reproductive Processes: A balanced microbiome is important for fertility as it helps create an environment conducive to sperm survival and movement.
What Are the Benefits of Vaginal Fluid?
Vaginal fluid serves multiple purposes, including:
- Lubrication: It reduces friction during intercourse, enhancing comfort and pleasure.
- Protection: The proteins and antibodies present help to defend against pathogens and maintain a balanced pH, reducing the risk of infections.
- Facilitation of Sperm Movement: Healthy vaginal fluid aids sperm motility, which is essential for successful fertilization.
- pH Regulation: Maintaining an acidic environment helps prevent harmful bacteria from proliferating.
- Nutritional Source: Vaginal fluid provides essential nutrients to sperm, supporting their viability and motility.
- Sexual Pleasure: Adequate lubrication enhances sexual pleasure, leading to a more satisfying experience for both partners.
Does Male Discharge Have Protein?
Just as vaginal fluid contains proteins, so does male semen. Seminal fluid is composed of sperm cells suspended in various fluids produced by seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands.
The Protein Content in Semen
The protein content in semen is significantly higher than in vaginal fluid, averaging about 5-7 grams per 100 milliliters. Key proteins in semen include prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and fibronectin, which support sperm function and viability.
The Role of Seminal Proteins
- PSA: This enzyme helps to liquefy semen after ejaculation, allowing sperm to swim more freely.
- Fibronectin: This protein aids in the adherence of sperm to the female reproductive tract, facilitating fertilization.
- Other Proteins: Semen contains various other proteins that contribute to the overall health of sperm and provide a nourishing environment.
Is Vaginal Fluid Safe?
Yes, vaginal fluid is generally safe. It contains natural substances that help maintain vaginal health. However, if you notice any unusual changes in color, odor, or consistency, it could indicate an infection or other health issue. Always consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Signs of a Healthy Vaginal Environment
A healthy vaginal environment is characterized by:
- Clear or milky discharge: Normal vaginal discharge can vary in appearance but should not be discolored.
- Mild odor: A subtle, natural scent is typical; a strong or foul odor may indicate a problem.
- Absence of irritation: Healthy vaginal fluid should not cause discomfort or irritation.
Is Semen Good Protein?
Semen does contain protein, but it should not be relied upon as a significant source of dietary protein. While it can provide some nutrients, including amino acids, the quantity is minimal compared to conventional protein sources like meat, dairy, and legumes.
Nutritional Analysis of Semen
In addition to protein, semen contains:
- Fructose: A simple sugar that provides energy for sperm.
- Zinc: Essential for maintaining sperm health and function.
- Vitamin C: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting sperm from oxidative stress.
Overall, while semen is a source of various nutrients, it is not a practical or reliable source of protein for dietary needs.
What Is Normal Protein in Females?
For adult females, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein varies depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health. Generally, women need about 46 grams of protein per day. This can be met through a balanced diet rich in protein sources like lean meats, dairy, nuts, and legumes.
Factors Affecting Protein Needs
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding have increased protein needs—up to about 71 grams per day to support fetal development and milk production.
- Age: Older women may require more protein to help maintain muscle mass and overall health, particularly as they age.
- Activity Level: Active women, especially those who engage in strength training or endurance sports, may need higher protein intake to support muscle repair and growth.
How Much Protein Do Women Need?
The protein requirements for women can change based on life stages. For example:
- Adult Women: About 46 grams per day.
- Pregnant Women: Approximately 71 grams per day to support fetal growth.
- Lactating Women: Similar to pregnant women, they require about 71 grams per day to ensure adequate milk production.
- Active Women: Depending on activity level, protein needs can increase significantly. Women who are very active might aim for 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
High-Quality Protein Sources
To meet protein needs, women should focus on high-quality protein sources, which include:
- Animal Products: Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products provide complete proteins containing all essential amino acids.
- Plant-Based Sources: Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent options, though some may need to be combined to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
What Fruits Can Boost Wetness?
Maintaining adequate hydration and incorporating certain fruits into your diet can enhance vaginal lubrication. Fruits that are particularly beneficial include:
- Watermelon: High in water content, which helps with hydration and contains citrulline, an amino acid that may promote blood flow.
- Avocados: Rich in healthy fats that support overall hormonal balance and help maintain vaginal health.
- Berries: Packed with antioxidants and water, they contribute to overall health and can support increased vaginal moisture.
Other Hydrating Foods
In addition to fruits, other hydrating foods can support vaginal wetness:
- Cucumbers: High in water content, they can help with hydration.
- Celery: Another hydrating vegetable that can contribute to overall fluid intake.
- Oranges: Rich in vitamin C and hydration, they can help maintain overall health.
What Foods Increase Female Wetness?
In addition to fruits, other foods can promote vaginal health and lubrication:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds provide essential fatty acids that are beneficial for hormone production.
- Dark Chocolate: Contains flavonoids that can enhance blood flow, potentially increasing sensitivity and lubrication.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are rich in nutrients that support hormonal health and overall well-being.
Foods to Avoid
While certain foods can enhance vaginal wetness, others may have the opposite effect:
- Caffeine: Can lead to dehydration, which may negatively affect vaginal lubrication.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to dehydration and may impact hormone levels.
- Processed Foods: High in sugar and unhealthy fats, these can disrupt hormonal balance and overall health.
How Can I Increase My Wetness Fast?
To increase vaginal wetness quickly, consider the following tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to ensure your body is well-hydrated.
- Foreplay: Engage in extended foreplay to stimulate natural lubrication. This not only increases wetness but also enhances sexual arousal.
- Use Lubricants: Water-based or silicone-based lubricants can help during intercourse if natural lubrication is insufficient.
- Warm Up: Engaging in intimate activities, such as kissing or massaging, can stimulate blood flow to the genital area and enhance natural lubrication.
How to Tighten Your Vagina Naturally?
To maintain vaginal tone and elasticity, consider the following:
- Kegel Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can enhance vaginal tightness. To perform Kegels, contract the muscles you would use to stop urination, hold for a few seconds, then relax. Aim for 10-15 repetitions, three times a day.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall body health, including pelvic muscle function. Focus on foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking can negatively impact blood flow and hormone levels, affecting vaginal health. Quitting smoking can lead to improved overall health and potentially better vaginal tone.
Why Is My Vagina Bringing Water?
Experiencing increased moisture or discharge can be completely normal, especially during ovulation or arousal. However, if the discharge is excessive, unusual in color, or accompanied by odor, it might be worth consulting a healthcare professional.
Understanding Normal vs. Abnormal Discharge
- Normal Discharge: Typically clear or milky in color, with a mild odor. Changes in discharge may be due to hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Abnormal Discharge: A strong odor, unusual color (green, yellow, or gray), or a cottage cheese-like consistency could indicate an infection such as bacterial vaginosis or a yeast infection. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice.
How Much Time Is Required to Discharge a Girl?
The time it takes for a female to reach orgasm and discharge varies greatly from person to person. Factors such as arousal, emotional connection, and physical stimulation play significant roles.
Understanding Female Arousal and Orgasm
- Arousal: Sexual arousal can take time and is often enhanced by emotional intimacy and physical stimulation. Women may take longer to become fully aroused compared to men.
- Orgasm: The time to orgasm can vary widely; some women may reach orgasm quickly, while others may take longer. The average time can range from a few minutes to over 20 minutes, depending on individual factors.
What Is Female Sperm Called?
While there is no distinct term for female sperm, the female reproductive fluid that aids in conception is often referred to as vaginal secretions or cervical mucus. This fluid plays a crucial role in providing a suitable environment for sperm and facilitating fertilization.
The Role of Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus changes in consistency and quantity throughout the menstrual cycle, becoming clearer and more slippery around ovulation. This change helps to:
- Facilitate Sperm Movement: The slippery texture aids sperm in swimming through the cervix into the uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization.
- Create a Favorable Environment: The right consistency of cervical mucus helps to protect sperm and create an optimal environment for conception.
Is Sperm Healthy to Eat?
Semen can be ingested and is generally considered safe, as it is made up of water, proteins, and nutrients. However, it is crucial to consider the potential for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) before engaging in such practices.
Nutritional Value of Semen
Semen contains various nutrients, including:
- Proteins: Important for tissue repair and immune function, though the amounts are small compared to dietary sources.
- Zinc and Vitamins: These contribute to overall health and support various bodily functions.
While it is safe to ingest semen for those in a monogamous relationship where both partners are free of STIs, it is not a recommended source of nutrition.
Is Vaginal Fluid Acidic?
Yes, vaginal fluid is typically acidic, with a pH ranging from 3.8 to 4.5. This acidity helps to create an environment that protects against harmful bacteria and infections.
The Importance of pH Balance
Maintaining the correct pH balance is crucial for vaginal health:
- Infection Prevention: An acidic environment helps to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast.
- Healthy Microbiome: The right pH supports the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as lactobacilli, which are vital for a healthy vaginal ecosystem.
Does Ovulation Discharge Have Protein?
Ovulation discharge, often described as clear and stretchy (similar to egg whites), does contain proteins that facilitate sperm movement. The composition of cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle, becoming more favorable for sperm passage during ovulation.
Understanding Ovulation and Discharge
During ovulation, the body produces more estrogen, which leads to changes in cervical mucus. The increased fluidity and stretchiness of the mucus help to:
- Enhance Sperm Survival: The mucus provides a nurturing environment for sperm, protecting them as they travel through the reproductive tract.
- Signal Fertility: The presence of clear, stretchy discharge is a sign of peak fertility, indicating that the woman is most likely to conceive.
Does Amniotic Fluid Have Protein in It?
Yes, amniotic fluid, which surrounds and protects a developing fetus, does contain proteins. These proteins play various roles, including providing nourishment to the fetus and contributing to lung development.
The Composition of Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic fluid is composed of:
- Water: The primary component, making up most of the fluid.
- Electrolytes: Important for maintaining osmotic balance.
- Proteins: Essential for fetal growth and development.
- Cells: Fetal cells shed into the amniotic fluid can provide valuable information for prenatal testing.
Where Is Female Arousal Fluid Made?
Female arousal fluid is produced in the vaginal walls and is stimulated by sexual arousal. The process involves increased blood flow to the vaginal area, which helps to produce lubrication.
The Physiology of Arousal
- Blood Flow: During arousal, blood vessels in the pelvic area dilate, increasing blood flow and leading to lubrication.
- Hormonal Influence: Hormones such as estrogen play a vital role in regulating the production of vaginal fluids.
- Psychological Factors: Emotional and mental stimulation can significantly influence the body’s ability to produce arousal fluid.
Nutritional Value of Female Juices
The nutritional value of female vaginal fluids, while not significant in terms of calories or macronutrients, does contribute to overall health. It is important to focus on a balanced diet for adequate nutrition.
The Role of Nutrition in Vaginal Health
A healthy diet supports vaginal health by:
- Supporting Hormonal Balance: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals contribute to hormonal balance.
- Enhancing Blood Flow: Foods that promote circulation, such as berries and dark chocolate, can enhance sexual function and arousal.
- Preventing Infections: A balanced diet supports the immune system, helping to prevent infections that can disrupt vaginal health.
Can You Get Protein from the Vagina?
While vaginal fluid does contain some proteins, it is not a viable source of dietary protein. It is essential to obtain protein from a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of food sources.
Understanding Dietary Sources of Protein
To meet daily protein needs, individuals should consider:
- Animal Sources: Such as chicken, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Plant Sources: Including beans, lentils, nuts, and whole grains.
Focusing on a balanced diet will ensure adequate protein intake for overall health and well-being.
How Much Protein Is in Female Discharge?
The protein content in female discharge can vary based on several factors, including hormonal changes and individual health. Generally, it is relatively low, contributing to overall fluid composition rather than being a significant source of protein.
Factors Influencing Protein Levels in Discharge
- Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle can affect the amount and composition of vaginal discharge.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions or infections may alter the protein content in vaginal fluids.
How Much Protein Is in Female Sperm?
The protein content in female reproductive fluids is minimal, and female sperm does not exist. Instead, it is the vaginal and cervical fluids that facilitate sperm movement and contribute to the overall reproductive environment.
The Role of Reproductive Fluids
While female reproductive fluids play a crucial role in supporting sperm, they do not contain sperm themselves. Instead, they create a nurturing environment for sperm to survive and successfully navigate the reproductive tract.
Does Sperm Have Protein?
Yes, sperm cells themselves contain proteins that are essential for their function. These proteins play roles in motility, fertilization, and overall sperm health.
The Importance of Sperm Proteins
- Motility: Proteins enable sperm to swim effectively, reaching the egg for potential fertilization.
- Fertilization: Certain proteins are involved in the binding and penetration of the egg during fertilization.
- Overall Health: Sperm proteins contribute to the viability and overall health of sperm cells.
What Happens If You Eat Discharge?
While it is generally safe to ingest vaginal discharge, it is important to consider individual health circumstances and potential exposure to sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Understanding the Risks
- STIs: If either partner is infected, there is a risk of transmitting infections through bodily fluids.
- Hygiene: Ensuring proper hygiene can help minimize the risk of infections. If there are any concerns about discharge, it is best to consult a healthcare professional.
Does Vaginal Discharge Smell?
Normal vaginal discharge has a mild, natural odor. However, a strong or unpleasant odor may indicate an infection or other health issues.
Identifying Abnormal Odors
- Normal Odor: A subtle scent is typical and should not be overpowering.
- Foul Odor: A strong, fishy odor can be a sign of bacterial vaginosis or other infections. If you notice any changes, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
Calories in Female Secretion
Vaginal fluids are not a significant source of calories. While they do contain some nutrients, they are not meant to provide energy in the same way as food does.
Understanding Nutritional Needs
To meet daily caloric needs, focus on a balanced diet that includes:
- Whole Foods: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.
- Adequate Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support overall health and wellness.
Conclusion
Understanding the composition and benefits of vaginal fluid is crucial for women’s health. While vaginal fluid does contain proteins, it is not a primary source of dietary protein. Instead, it plays essential roles in lubrication, protection, and facilitating reproductive processes. By focusing on overall health, hydration, and nutrition, women can support their vaginal health and enhance their well-being. Remember, if you have concerns about vaginal health or experience unusual symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and support.




Your blog is a treasure trove of knowledge! I’m constantly amazed by the depth of your insights and the clarity of your writing. Keep up the phenomenal work!
I’ve been following your blog for some time now, and I’m consistently blown away by the quality of your content. Your ability to tackle complex topics with ease is truly admirable.
“Well explained, made the topic much easier to understand!”
Your writing is like a breath of fresh air in the often stale world of online content. Your unique perspective and engaging style set you apart from the crowd. Thank you for sharing your talents with us.